Effective IT roadmapping, budgeting, and planning are key to any business that seeks to be competitive. These processes align technology with long-term goals, optimize spending, and support informed decision-making. A well-structured IT strategy reduces the risk of unexpected disruptions and provides a clear roadmap for growth. By shifting from a reactive to a proactive approach, businesses can better manage resources, avoid costly surprises, and stay ahead of potential risks and opportunities. A Strategic IT road map brings focus to a business by enabling a visible timeline of investments in technology, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and that the right technology decisions are made at the right time. To stay ahead, companies should plan at least three years in advance, even if the exact details are not yet known, allowing for proper strategic planning and budgeting to support future initiatives.
What Is IT Roadmapping and Why Is It Essential?
The biggest misconception when creating an IT roadmap is that it becomes too focused on technology. Technology is only part of the equation; it exists to support the business’s goals. The key question is: What is the business trying to achieve? Where are we trying to go? Technology helps achieve these objectives, whether it’s by adding new capabilities or mitigating risks.
This means that the IT person responsible for developing the strategy must have a deep understanding of the business itself. They need to grasp the company’s mission, vision, and strategic goals to ensure alignment. The roadmap must be designed to drive the business forward, not just to implement technology for the sake of technology.
“IT road mapping is the strategic process of outlining your organization’s technology initiatives, projects, and investments on a timeline with an alignment towards the greater goals and objectives of the organization.”
It serves as a dynamic tool that aligns IT strategy with business goals, helping to visualize how the technology landscape will evolve over time. The roadmap provides a high-level overview of upcoming IT projects, investments, and potential challenges, making it easier for both technical and non-technical teams to understand and plan accordingly.
Key Components of an IT Roadmap
- Executive Summary
This section drills into the specifics of each project. Here, businesses outline cost estimates for hardware, software, services, and recurring monthly expenses. These estimates are crucial for budgeting purposes but are subject to change as project scopes evolve.
- Timeline
The timeline is the backbone of an IT roadmap, offering an overview of key IT projects and expenses. It helps businesses forecast capital expenditures (CapEx) and operational expenses (OpEx) for the upcoming months and years.
- Budget Planning
Budgeting is a core component of the IT roadmap. This section sums up the expected costs for each initiative, helping to integrate these estimates into the company’s overall budget planning process. By incorporating the roadmap into regular financial reviews, businesses can ensure funds are available when needed and avoid cash flow issues.
The Strategic Planning Process
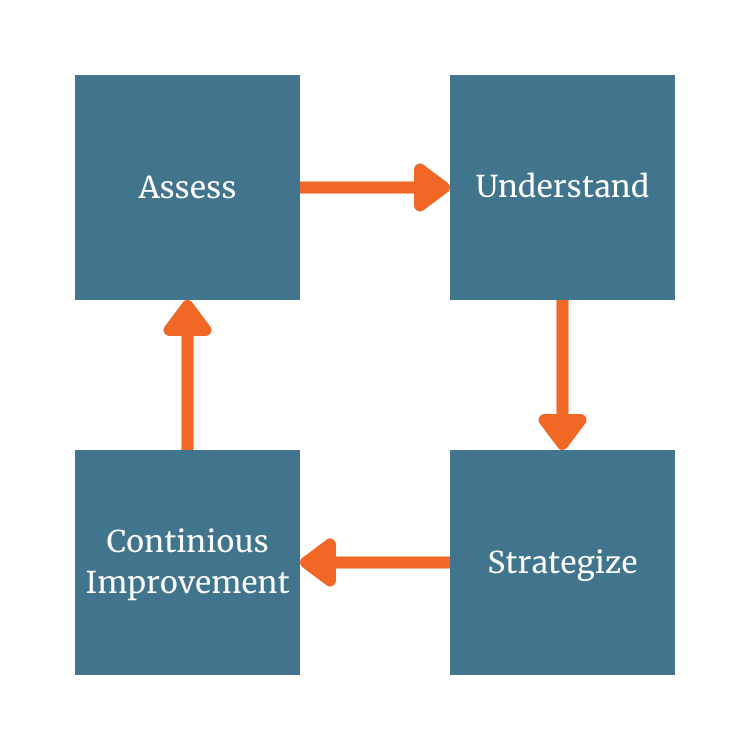
A successful IT roadmap follows a structured, multi-phase approach: assess, understand, strategize, and continuously improve.
- Assess the current state of IT and business needs.
- Understand the organization’s goals and where the business aims to go.
- Strategize by identifying IT initiatives that can help meet these goals, such as projects to reduce risks or increase productivity.
- Continuous Improvement ensures that the roadmap is adaptable as the business and technology landscapes evolve.
How to Create a Practical IT Roadmap
When developing a strategic IT roadmap, it’s essential to align your technology strategy with your overall business objectives. Begin by identifying the critical IT projects needed to support these goals. From there, break down each project into smaller, manageable tasks, detailing costs, timelines, and resources. It’s important to involve key stakeholders, particularly from finance and operations, to ensure the roadmap aligns with the business’s financial capabilities.
Planning the IT Roadmap for the Long Term
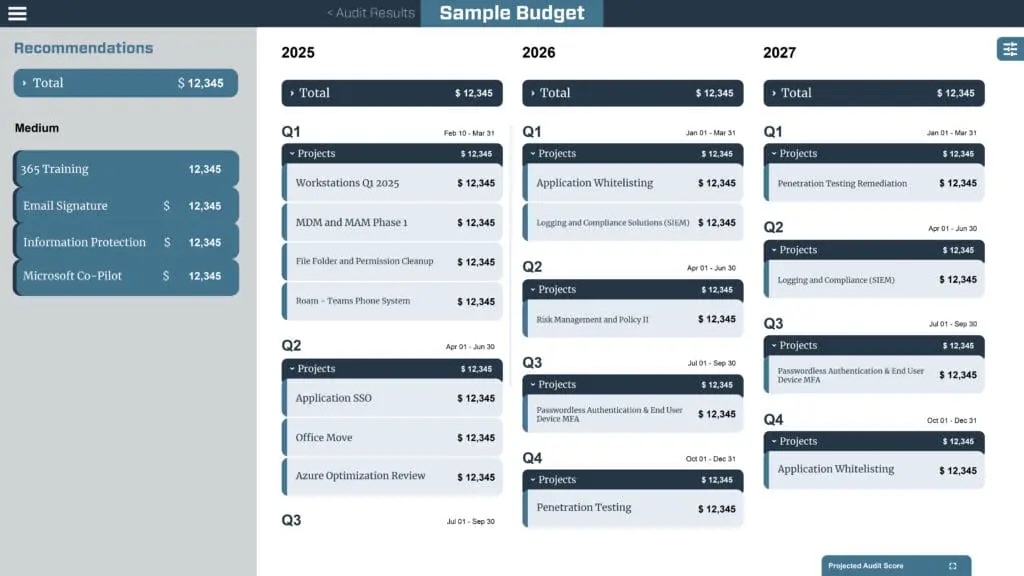
Planning an IT roadmap for the next three years helps avoid surprises and ensures proper budgeting and planning for future projects, even if the exact details are not fully known in advance. During the planning phase the roadmap should include all recommendations with scope and budget for the year. While not all recommendations may be approved from the planning stage, the goal is to ensure that everything planned for the year is incorporated into the final roadmap with an approved budget. This approach allows businesses to plan ahead while executing current year initiatives.
Budgeting for IT: A Proactive Approach
IT budgeting should not be a reactive process. Instead, it should be approached with a proactive mindset that incorporates anticipated technology needs. By aligning IT budgets with the roadmap, businesses can manage expenditures more effectively. This includes both capital investments in IT infrastructure and the operational costs associated with ongoing software licenses, support services, and system updates. A well-thought-out IT budget accounts for known costs while leaving room for future growth and unexpected expenses.
Lifecycle Asset Management and Business IT Roadmaps
Including lifecycle asset management in your Business IT roadmap is vital to maintaining an efficient and cost-effective IT environment. Assets like servers, workstations, and network devices have limited lifespans, and it’s important to replace them before they reach their end-of-life. By planning for these replacements ahead of time, businesses can avoid system downtime and ensure their IT infrastructure stays current and reliable.
Strategic Projects in Your IT Roadmap
In addition to lifecycle assets, your technology roadmap should include strategic initiatives that are aligned with your business’s long-term vision. These initiatives may involve software upgrades, new business applications, or security enhancements. While these initiatives may require significant upfront investment, they are essential for staying competitive and addressing evolving business needs.
Monitoring and Adjusting the IT Roadmap
An IT roadmap is a living document that should be reviewed regularly. As new technology trends emerge, or business priorities shift, your roadmap must adapt to reflect these changes. By continuously monitoring and updating the roadmap, businesses can ensure they are prepared for the future while staying agile enough to adjust when necessary.
Conclusion: A Roadmap for Success
Strategic IT roadmapping, budgeting, and planning are indispensable practices for businesses looking to grow and evolve in a digital landscape. By taking a proactive, strategic approach to IT investments, organizations can avoid costly surprises, optimize resources, and create a technology infrastructure that supports long-term success. Whether you’re planning for technology refresh cycles or embarking on major digital transformation initiatives, a well-defined IT roadmap ensures your business stays on track toward its goals.
Need help building a strategic technology roadmap? Contact us, and one of our representatives will reach out for a free consultation














